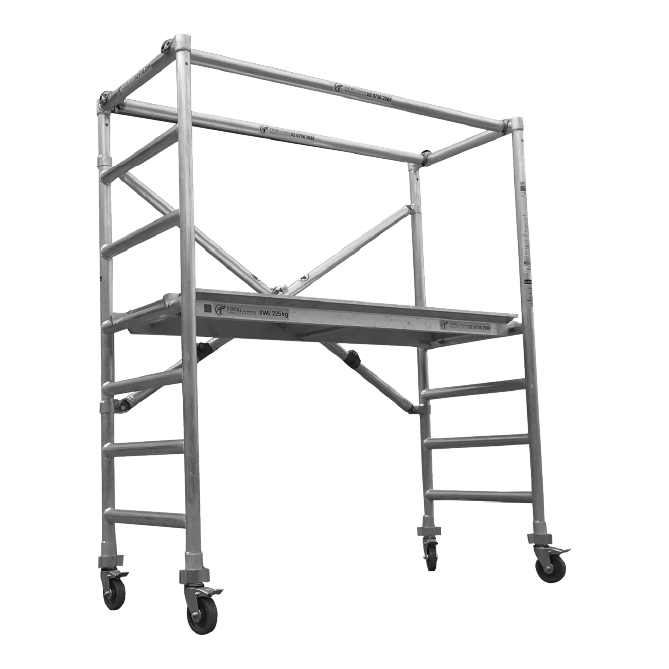
A solid scaffold site checklist keeps every part at hand before work begins. Having the right scaffolding components ready prevents project delays and keeps crews safe at height. From the core framework to safety rails, knowing each element’s job helps you assemble a robust system. This guide covers the ten vital scaffolding parts every builder relies on.
1. Scaffolding Planks
Planks create the working surface where tradespeople stand and move materials. Steel planks handle heavy loads and harsh conditions, while timber variants suit lighter tasks and can absorb shocks. Laying these boards on the primary and intermediate transoms keeps them level. Checking each plank for warping or cracks before use ensures a stable deck that won’t sag underweight.
2. Scaffold Tubes
Scaffold tubes form the framework’s backbone, linking horizontal and vertical runs to support decks, rails, and braces. Galvanised steel tubes resist corrosion even with regular outdoor use. Standard lengths slot into place with scaffold fittings. Tools, couplers, and ledgers secure adjacent tubes so the structure stays rigid. Stocking extra tubes and connectors guards against setbacks if pieces get damaged or need shortening.
3. Sole Boards
Also known as sole plates, these boards slide beneath base plates to extend pressure distribution. Timber sole boards suit soft ground, while steel options resist moisture and decay. Installing sole boards first ensures the scaffold remains level and stable, especially on uneven or sloping terrain, keeping all standards upright.
4. Swivel Couplers
Swivel couplers join tubes at right angles while allowing rotation for precise positioning. Unlike fixed couplers, swivel types adapt to angled bracing or complex corners. Including various couplers in your scaffold fittings assortment tools guarantees you can connect tubes wherever needed, whether tying into existing structures or creating free-standing frames.
5. Base Plates
Base plates sit under each vertical support, spreading the load over a wider ground area to prevent sinking into loose soil. These plates pair with sole boards to balance the scaffold on uneven surfaces. A firm base plate setup stops leaning and maintains the entire scaffold’s integrity, which is critical when shifting loads come into play.
6. Toe Board
A toe board secures along platform edges, catching dropped tools or debris that might otherwise fall to the ground level. These low barriers work alongside guardrails to shield people below. Installing toe boards on every active deck meets safety regulations and keeps your site incident-free.
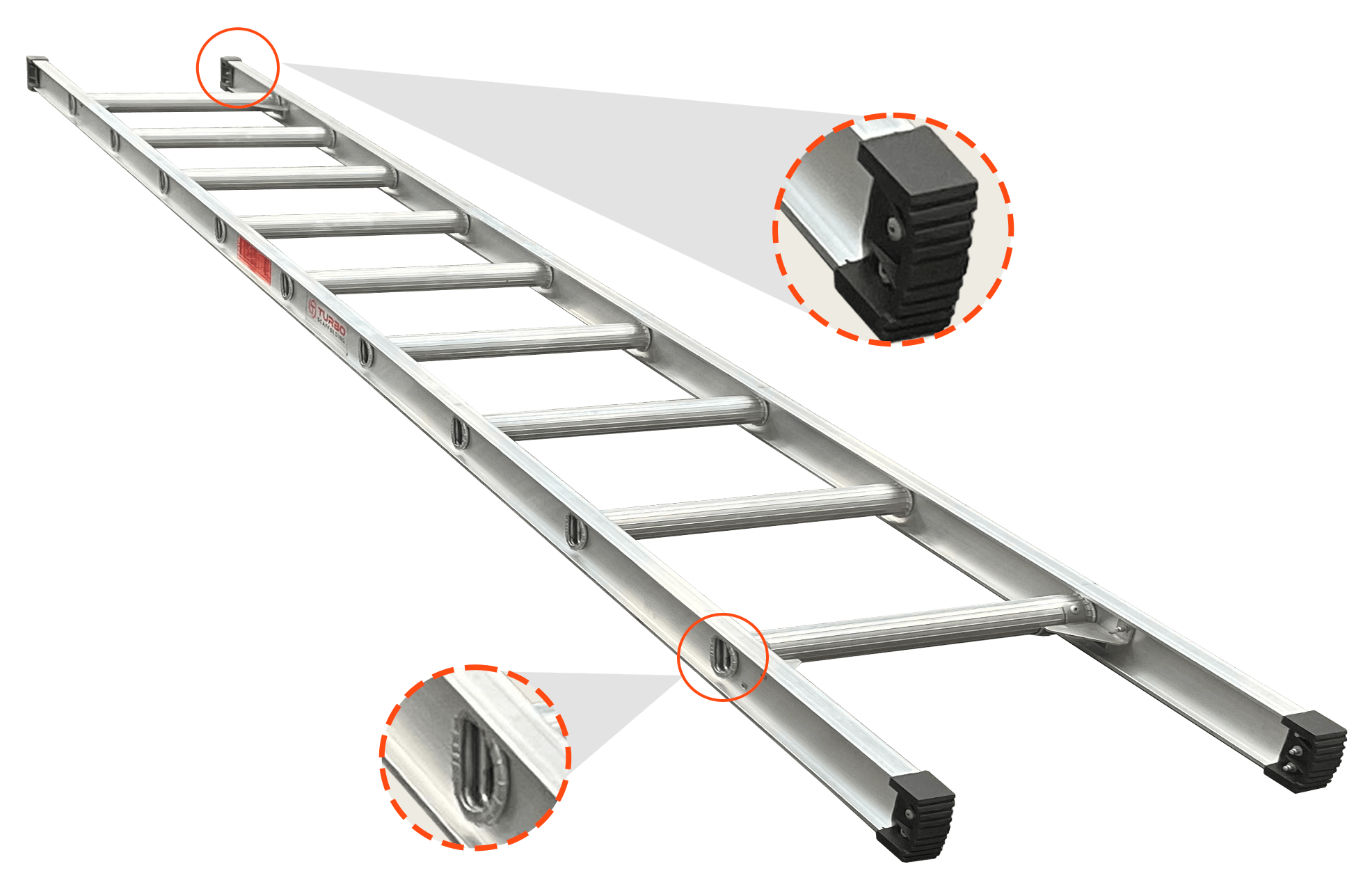
7. Ladder Access
Providing a proper ladder stops workers from resorting to unsafe climbing methods. Fixed rung ladders attach safely to the scaffold frame, offering a consistent climb angle and solid handholds. Access towers feature built-in ladders with handrails and toe boards for taller setups. Safe access to every level speeds up material movement and prevents fall injuries.
8. Standards
Standards are the vertical tubes carrying compression loads from the deck and any materials or workers above. Spaced at intervals determined by load calculations, standards keep the scaffold upright. Steel standards offer high compressive strength, whereas aluminium standards cut weight for easier handling. On every project, extra standards help you extend height or replace any dented pieces swiftly.
9. Transoms
Primary and intermediate transoms run horizontally between standards, supporting the planks above. Main transoms bear heavy loads, while intermediates add reinforcement for wider spans. Primary transoms support the heaviest loads, and intermediate transoms reinforce wider sections. If needed, ledgers anchor the scaffold to the building face. Keeping spare transoms and ledgers on hand allows you to adjust spans immediately.
10. Security Components
Safety rails and diagonal braces work together to prevent falls and resist sway. Guard rails are fixed along the platform’s open sides, while braces lock the whole arrangement into a rigid shape. A right-angle and swivel coupler pattern ensure braces remain tensioned under wind or shifting loads. Complete your scaffold site checklist by confirming every rail and brace is secured.
Benefits of Temporary Fencing for Your Scaffolding
Adding temporary fencing around scaffold zones creates clear site boundaries, restricts unauthorised access, and guides foot traffic. Panels link easily to ledgers and standards with couplers, forming a secure perimeter. Pairing fencing with scaffold netting, controls dust and debris while giving space for signage or branding. Local scaffold supplies in Brisbane often include matching fencing and netting packages for quick setup.
Scaffolding Parts Inspection and Upkeep
Why Regular Inspections for Scaffolding are Imperative?
Daily and pre-use inspections catch faults before they cause harm. Checking every tube, plank and connection against your scaffold site checklist verifies compliance with safety standards. After any assembly changes or severe weather, a fresh inspection ensures no component has loosened or shifted.
Watch Out for the Common Issues During Inspections
Watch for corrosion on rails, cracks in planks, stripped threads on couplers and bent tubes. Loose or missing pins in scaffold fittings tools reduce load capacity. A quick spot-check of each base plate and sole board confirms the scaffold remains level and seated correctly.
Tips for Upholding Scaffolding Parts for Long Life
Regular Cleaning: Rinse tubes, ledgers, and planks to remove mud, concrete splatter, and debris. Keeping surfaces clean prevents grit from wearing against couplers and reduces the chance of slipping during assembly.
Rust Prevention: Inspect for surface rust on steel parts and treat affected areas with a rust-inhibiting spray or primer. Rust can weaken metal over time, so tackling it extends the life of your entire scaffold.
Covered Storage: It is vital to store scaffold supplies under roofed or tarpaulin-covered areas. Protecting couplers, tools and boards from rain and sun prevents warping and corrosion during downtime.
Follow Manufacturer’s Guidelines: Respect load ratings stamped on standards and transoms, and adhere to maximum span charts. Overloading components leads to premature fatigue and potential collapse risks.
Gentle Handling: When dismantling, lower tubes and planks rather than dropping them. Impact can cause hidden dents or cracks that compromise tube strength.
Weight Awareness: Track tools and materials on decks and don’t exceed the rated capacity. Distributing loads correctly with ledgers and transoms ensures no area bears too much weight.
Quick Replacement: Have a ready stock of standard parts—tubes, planks, couplers, and braces. It will help with swapping worn or damaged items immediately. Swapping before failure keeps everyone safe.
Detailed Record-Keeping: Log inspection dates, findings, and any part replacements, which will help maintain clear records, spot recurring issues, and support compliance audits.
Maintaining quality scaffolding parts and adhering to a thorough scaffold site checklist guarantees safe, efficient builds. Keeping extras of critical items—including ledgers, couplers, and other scaffold-fitting tools—means your team stays on schedule and on solid ground.
Are you looking for high-quality scaffolding or reliable scaffold fittings tools? Contact Turbo Scaffolding today!